HDPE polymerization process: Slurry, Gas-Phase, and Solution

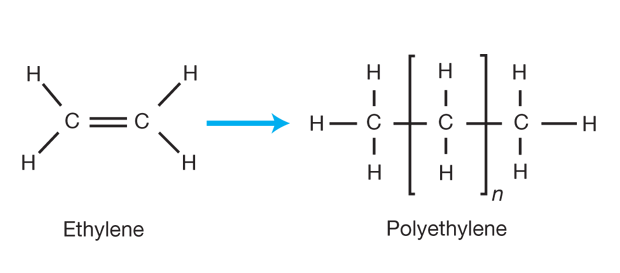
High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) is one of the most important plastics in the modern world. Its strength, chemical resistance, and cost-effectiveness make it essential for HDPE pipes, HDPE films, blow-molded bottles, and packaging materials. However, the properties of HDPE depend largely on the HDPE polymerization process used in its production.
Industrial manufacturers mainly rely on three HDPE production processes: slurry process, gas-phase process, and solution process. Each has distinct advantages, costs, and applications, making them suitable for different HDPE grades.
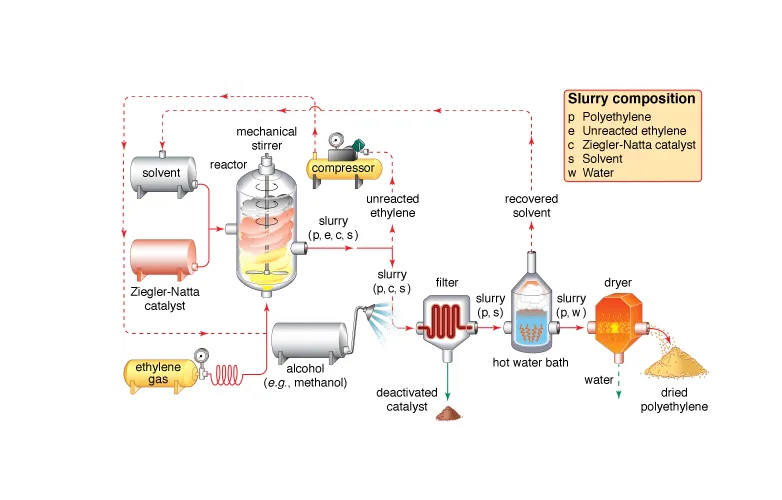
-Slurry Process for HDPE
The slurry process (also called suspension polymerization) is a widely used HDPE polymerization process. In this method, ethylene is polymerized in a liquid hydrocarbon medium like hexane or isobutane. The polymer forms as solid particles suspended in the liquid, which makes recovery and recycling straightforward.
Slurry Process Features:
Temperature: 80–110 °C
Pressure: 5–30 bar
Catalysts: Ziegler–Natta and Chromium catalysts
Produces HDPE with narrow molecular weight distribution
Advantages of Slurry Process:
Proven and reliable technology.
Simple solvent separation and recycling.
Produces strong HDPE grades for pipes and blow molding.
Applications:
HDPE pipe grades (PE80, PE100) for water and gas distribution.
Blow-molded containers, bottles, and industrial drums.
The slurry polymerization process for HDPE is especially preferred in applications where strength and stiffness are crucial.
-Gas-Phase Process for HDPE
The gas-phase process is the most flexible and widely adopted HDPE polymerization process today. In this method, ethylene gas, hydrogen, and comonomers are fed into a fluidized bed reactor. The catalyst particles remain suspended in the gas stream, and polymer granules are continuously withdrawn.
Gas-Phase Process Features:
Temperature: 70–110 °C
Pressure: 10–30 bar
Catalysts: Ziegler–Natta or Metallocenes
Produces a wide variety of HDPE grades
Advantages of Gas-Phase Process:
No solvents required, reducing costs and environmental impact.
Highly flexible for HDPE film grades, HDPE injection molding grades, and HDPE pipe grades.
Continuous and efficient operation.
Applications:
HDPE film grades (e.g., HDPE 7000F) for packaging, grocery bags, and wrapping films.
HDPE bottles and containers through blow molding.
Injection-molded products such as crates and industrial parts.
The gas-phase HDPE polymerization process is particularly dominant in packaging and film production due to its efficiency.
-Solution Process for HDPE
The solution process is a high-temperature and high-pressure HDPE polymerization method. Ethylene is dissolved in a hydrocarbon solvent, creating a homogeneous mixture. On cooling, the polymer precipitates out.
Solution Process Features:
Temperature: 130–270 °C
Pressure: 30–60 bar
Catalysts: Ziegler–Natta, Chromium, or Metallocenes
Produces HDPE with broad or bimodal molecular weight distribution
Advantages of Solution Process:
Produces specialty HDPE grades with tailored performance.
Excellent control over strength and durability.
Disadvantages:
Higher energy consumption.
More costly due to solvent recovery requirements.
Applications:
High-performance HDPE pipe grades (PE100N, P6006).
Geomembranes and specialty films.
Industrial products requiring exceptional durability.
The solution polymerization process for HDPE is often chosen when superior mechanical properties are required.
🔹 Comparison of HDPE Polymerization Processes
| Feature | Slurry Process | Gas-Phase Process | Solution Process |
|---|---|---|---|
| Reaction Medium | Liquid hydrocarbon | Gas (fluidized bed) | Hydrocarbon solvent |
| Temperature (°C) | 80–110 | 70–110 | 130–270 |
| Pressure (bar) | 5–30 | 10–30 | 30–60 |
| Catalyst Used | ZN / Cr | ZN / Metallocene | ZN / Cr / Metallocene |
| Cost Efficiency | Medium | High (low-cost) | Low (high-cost) |
| Typical HDPE Grades | Pipes, blow molding | Films, bottles, pipes | Specialty HDPE |
The HDPE polymerization process plays a critical role in defining the properties of HDPE grades.
The slurry process is ideal for HDPE pipes and blow molding applications, offering strong and reliable materials.
The gas-phase process is the most economical and versatile, dominating HDPE film and packaging markets.

